Laboratory for Immune Cell Systems
Welcome to the Laboratory for Immune Cell Systems
The immune system is pivotal not only for fighting against various infections but also for regulating the homeostasis of numerous tissues and organs. Our research group studies the role of innate lymphoid cells (ILCs), lymphocytes that lack antigen specific receptor. Among ILCs, our group focuses on group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2), which was originally named natural helper (NH) cells, a new innate lymphocyte population that we identified in 2010.
ILC2 are distinct from previously known lymphocytes such as T cells, B cells, and NK cells. ILC2 are abundantly present in fat-associated lymphoid clusters (FALC) and express c-Kit and Sca-1 but are negative for lineage markers, which are expressed on various hematopoietic cells. ILC2 also express several cytokine receptors such as IL-2R, IL-7R, IL-25R and IL-33R. IL-25 and IL-33 are known to induce type 2 immune responses during helminth infection and allergic inflammation. NH cells constitutively produce IL-5, IL-6 and IL-13 and produce large amounts of IL-5 and IL-13 in response to a combination of IL-2 + IL-25 or IL-33 alone, which induces eosinophilia and goblet cell hyperplasia that exacerbate allergic symptoms.
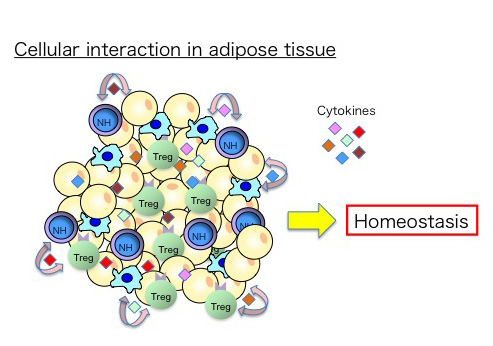
Adipose tissues are important in the storage and consumption of energy but inflammation in adipose tissue resulting from a failure in homeostatic mechanisms leads to insulin resistance and eventually the onset of diabetes. Adipose tissues contain several immune cell types including ILC2, macrophages and regulatory T cells (Treg). Treg cells are important in the maintenance of immune homeostasis in many tissues. Treg cells in adipose tissues are unique in that they express receptors for IL-33 and unlike Tregs in lymphoid tissues, Tregs in adipose tissues are maintained by IL-33. Macrophages are classified into two functionally distinct types, pro-inflammatory M1 and anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages. Infiltration of M1 macrophages and CD8+ T cells are associated with adipose tissue inflammation but M2 macrophages play an important role in the maintenance of homeostasis of adipose tissues. M2 macrophages are induced by type 2 cytokines such as IL-4 and IL-13, suggesting the involvement of NH cells in the induction of M2 macrophages.