Laboratory for Immune Cell Systems
Current research
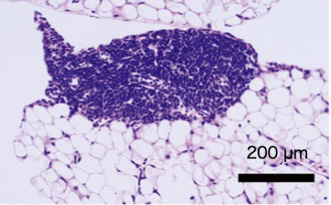
Role of ILCs in the homeostasis of adipose tissues
ILC2 were originally found in the FALC structure in adipose tissues. It has been shown that numerous immune cells, including macrophages, play important roles in the homeostasis of adipose tissues and that failure of homeostatic regulation in adipose tissues leads to various diseases including insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. We are therefore interested in the role of ILC2 in the homeostasis of adipose tissues. ILC2 constitutively produce the type 2 cytokines IL-5 and IL-13 that are known to act on various immune cells such as macrophages and eosinophils. In addition, regulatory T cells (Treg) are relatively abundant in adipose tissue and are likely involved in the homeostasis of adipose tissue. We study the function of ILC2, Tregs and macrophages in obesity-induced inflammatory responses in adipose tissues to elucidate their role in adipose tissue. We have shown that Tregs present in adipose tissue but not lymphoid tissue express IL-33 receptors and IL-33 plays a critical role in the maintenance of Tregs in adipose tissues.