Laboratory for Transcriptional Regulation
Current research
1. Lineage specification and commitment during T lymphocytes development
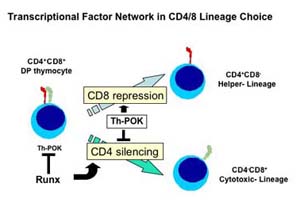
Developmental programs in metazoan species present daunting challenges of spatial and temporal control over gene expression. The two major lineages of abT lymphocytes, helper and cytotoxic T cells, differentiate from common progenitor CD4+CD8+ DP thymocytes. While cells expressing class II-restricted TCR differentiate into helper lineage and cease CD8 expression, cells expressing class I-restricted TCR differentiate into cytotoxic linage and silence CD4 expression.
However, the molecular pathways that govern cell fate determination of CD4+CD8+ DP thymocyte are not well understood. Lineage decisions of CD4+CD8+ DP thymocytes toward the CD4-CD8+ cytotoxic- or CD4+CD8- helper- lineage correlate with the cessation of Cd4 or Cd8 gene expression, respectively. Therefore, mechanism that regulates expression of co-receptor genes would share a common regulatory pathway with mechanism that regulates cell fate determination of CD4+CD8+ DP thymocytes.
The lineage specific expression of Cd4 gene is controlled by the intronic silencer. We have identified Runx transcriptional factor family as CD4 silencer binding protein, and have shown that Runx3 plays major roles in establishment of cytotoxic lineage specific CD4 silencing. On the other hand, current genetic approaches have demonstrated that expression of a functional ThPOK transcriptional factor is essential and sufficient for helper T cell development. Therefore, it is curious to examine relationship between Runx and ThPOK factors. By using several mutant mouse strains harboring mutations at Runx family genes, we have found a crucial antagonistic interplay between Thpok and Runx in controlling helper versus cytotoxic lineage decision by CD4+CD8+ DP thymocytes. We are now investigating how expression of these factors are controlled under TCR signals.
Runx complex have been shown to be involved in many developmental pathway beyond species. However, function of Runx complex in development and regulation of immune system has not been well addressed mainly due to lethal phenotype of germline knockout mice. In addition to the conditional knockout mice, we recently generated isoform specific knockout and knock-in mutant mice of Runx family genes. By analyzing these mutant mice, we try to reveal novel roles of Runx complex in development and regulation of immune system.